|
|
|
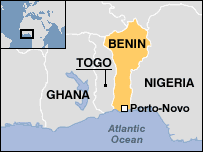
Benin is situated in
West Africa and is bounded to the east by Nigeria,
to the north by Niger and Burkina Faso, and to the
west by Togo. Benin's shoreline now includes what
used to be known as the Slave Coast, from where
captives were shipped across the Atlantic. Elements
of the culture and religion brought by slaves from
the area are still present in the Americas, for
example the voodoo cult in Haiti.
Before being colonised by France towards the end
of the 1800s, the area comprised several independent
states, including the Kingdom of Dahomey, which had
a well-trained standing army and was geared towards
the export of slaves and later palm oil.
The first years of full independence from France
in 1960 were marked by instability, and the initial
years of Mr Kerekou's rule featured Marxism-Leninism
as the official ideology.
However, during the 1980s Mr Kerekou resigned
from the army to become a civilian head of state and
liberalised the economy.
Since then Benin has a new president, Yayi Bonu
who was elected in 2006.
While Benin has seen economic growth over the
past few years and is one of Africa's largest cotton
producers, it remains among the world's poorest
countries. The economy relies heavily on trade with
neighbouring Nigeria.
Key Facts:
- Population: 7.1 million (UN, 2005)
- Capital: Porto-Novo
- Area: 112,622 sq km (43,484 sq miles)
- Major languages: French (official) Fon,
Ge, Bariba, Yoruba, Dendi
- Major religions: Indigenous beliefs,
Christianity, Islam
- Life expectancy: 48 years (men), 53
years (women) (UN)
- Monetary unit: 1 CFA (Communaute
Financiere Africaine) franc = 100 centimes
- Main exports: Cotton, Palm Oil
|
 |
|
 | |
|
| |



